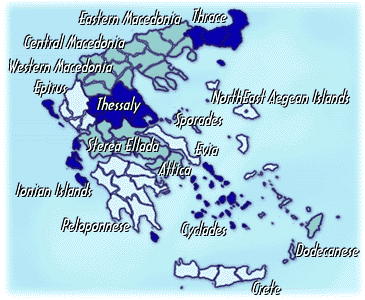
 The Greek peninsula, Europe's southeastern tip, occupies an area of 131,944 square
kilometres, and consists of mainland Greece (Attica, Peloponnese, Sterea
Ellada, Thessaly, Epirus, Macedonia [Central, Western, & Eastern], Thrace) and the islands of the Aegean and Ionian
seas. The Greek peninsula, Europe's southeastern tip, occupies an area of 131,944 square
kilometres, and consists of mainland Greece (Attica, Peloponnese, Sterea
Ellada, Thessaly, Epirus, Macedonia [Central, Western, & Eastern], Thrace) and the islands of the Aegean and Ionian
seas.
Geographically, it belongs to Europe, since it forms the most southerly
extremity of the Balkan peninsula, but it has another special link to
Europe through the cluster of Ionian islands which form a chain off Greece's western shores, in the Ionian sea.
In
contrast there are numerous islands in the Aegean sea, some isolated
like Crete in the South, and some in groups like the islands of the Northeast Aegean, the Sporades, the Cyclades, and the Dodecanese.
The Cyclades consist of 39 islands of which only 24 are inhabited. The
Sporades lie off the eastern shores of mainland Greece and Euboea (Evia)
and retain their genuine island characteristics and unchanged local traditions.
The Dodecanese group consists of twelve major islands and a number of smaller
ones, each with its own distinctive features and peculiarities. Finally,
the Saronic Gulf which is the stretch of sea linking the shores of Attica
to those of the Peloponnese, contains another group of small islands which
adds its own colour to the general surroundings.
|







